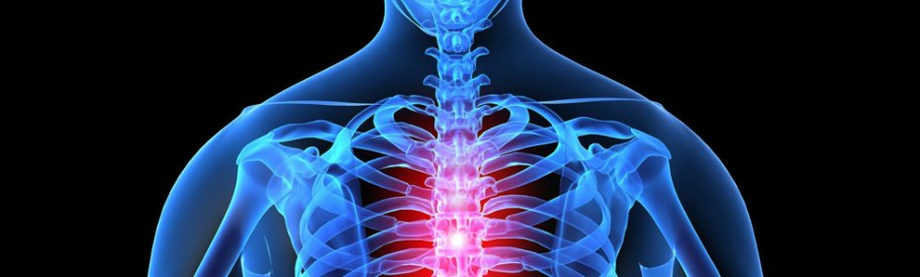
Osteochondrosis is a disease of the spine, characterized by the development of degenerative-dystrophic changes in bone and cartilage tissue in one or more of its departments. The development of thoracic osteochondrosis is much less common than similar manifestations in the cervical and lumbar spine. This is due to the peculiarities of the anatomical structure of the median part of the human back, where the mobility of the vertebrae is somewhat limited. This significantly reduces the likelihood of injury. A couple of decades ago, this type of osteochondrosis was more common in older people. Today, the disease also affects younger men and women. Children are no exception.
Description
Osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine is a disease of the skeletal system, characterized by damage to the intervertebral discs, vertebrae and their degenerative changes. In the first stage of the disease, the manifestations are mild, which is an obstacle to early diagnosis. However, over time, the disease progresses.
Gradually, the ligamentous apparatus is also involved in the process. A little less frequently complications develop, manifested in the form of atrophy of muscle tissue and accompanied by a decrease in sensitivity and functional disorders of internal organs.
In advanced cases, with thoracic osteochondrosis, the cartilage and bones begin to break down. At the same time, premature aging of the musculoskeletal system is noted.
Against the background of this disease, diseases such as:
- prostatitis;
- pneumosclerosis;
- atrophy of the organs of the reproductive system, which often leads to infertility;
- atherosclerosis;
- cancerous tumors.
According to medical statistics, thoracic osteochondrosis of the spine occurs equally in men and women.
Symptoms of the disease
Thoracic spine osteochondrosis has a number of specific features, including:
- chest pain that occurs when the body is thick and for a long time in one position;
- pain syndrome with increased physical exertion, for example, when lifting weights;
- the occurrence of difficulty in inhaling and exhaling, accompanied by a sensation of squeezing in the central part of the back;
- constant aching pain in the shoulder blades;
- numbness of some parts of the body;
- prolonged cold sensation that occurs periodically, accompanied by chills;
- decrease in body temperature in the legs;
- itching and burning in the lower limbs.
With impaired functions of the vascular system of the thoracic spine, patients have a number of characteristic signs:
- peeling of the skin;
- thin and brittle nails;
- abdominal pain, flatulence;
- stool disorders, in which bouts of diarrhea can be replaced by constipation;
- nausea, heartburn;
- symptoms of intercostal neuralgia;
- decreased sexual activity.
With thoracic osteochondrosis, there are two types of pain syndrome:
- Back pain (back pain).
- Dorsago (back).
The first is characterized by prolonged pain in the areas of damage to the vertebrae and intervertebral discs. The second is intense paroxysmal pain of an acute nature, accompanied by a feeling of muscle stiffness and difficulty in breathing.
One of the complications accompanying osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine is gastritis, or rather its exacerbations, characterized by pain in the epigastric region.
Causes of osteochondrosis
The development of osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine is due to pathological changes that occur in the intervertebral discs. The causes of this disease can be:
- hereditary predisposition;
- hernia, disc deformity;
- formation of osteophytes;
- destruction of cartilage;
- insufficient blood supply to the spinal canal, which has developed due to blockage of the conducting vessels and arteries;
- degeneration of bones, cartilage and muscle tissue caused by a poorly distributed load on the spine;
- metabolic disorders caused by calcium deficiency in the body.
The factors that act as the cause of pathological changes are:
- lifting heavy objects;
- sedentary work;
- long stay in one position;
- uneven load on the spine;
- spinal injury;
- scoliosis.
Thoracic osteochondrosis is often diagnosed in professionals involved in power sports.
Diagnostics
Thoracic osteochondrosis requires mandatory diagnosis and differentiation with other diseases that have similar symptoms. Through an in-depth examination, the following are excluded:
- angina;
- heart attack;
- lung inflammation;
- pathology with gastric symptoms.
This way you can avoid misdiagnosis. Assessment of the patient's condition is carried out on the basis of the anamnesis, taking into account all the symptoms of the disease and the patient's complaints.
To confirm the diagnosis, clarify the location of the affected areas, identify benign neoplasms and cancerous tumors, progressive instrumental methods are used:
- radiography;
- TC;
- magnetic resonance.
To determine the degree of the inflammatory process in osteochondrosis, blood and urine tests are prescribed.
Treatment
The treatment regimen for thoracic osteochondrosis is developed individually. Chondrosis refers to those diseases that can provoke disruption of internal organs, so it must be treated.
In this case an integrated approach is needed. Medical therapy is mandatory.
Conservative treatment
Patients are prescribed painkillers and drugs with an anti-inflammatory spectrum of action. With the help of these drugs, relieving pain and reducing inflammation, the mobility of the vertebrae in the thoracic region is ensured. Acute manifestations are quickly stopped by injection.
In parallel, to improve the condition of bones and cartilage, chondroprotectors, minerals and vitamin complexes are prescribed.
Removal of muscle spasms is provided by muscle relaxants.
To accelerate the effect, you can use therapeutic ointments and creams for external use.
Patients undergo paravertebral blockages, with the help of which it is possible to reduce pain. The injectable solutions contain corticosteroids and antiseptics.
It is impossible to cure thoracic osteochondrosis with drugs alone. We are talking about such measures as lifestyle correction, proper nutrition, massage, physical therapy and other methods. It is quite possible to speed up the recovery process if physiotherapeutic procedures are included in the treatment regimen: magnetotherapy, laser, vacuum therapy, traction method, etc.
In case of ineffectiveness of drug treatment, patients can be prescribed surgery. Sometimes surgery is the only option. Absolute indications for surgery are spinal instability, canal stenosis or spinal hernia.
Organization of proper nutrition
With osteochondrosis, a salt-free diet is provided. In addition, it is necessary to exclude spicy, fatty, fried foods, smoked meats, alcohol, carbonated drinks, coffee; limit the use of sugar, spices and mayonnaise.
Otherwise, the diet should be as balanced as possible and contain all the vitamins and minerals aimed at improving the functioning of the musculoskeletal system.
The daily menu should include foods rich in calcium and phosphorus. This list includes cottage cheese, hard cheeses, milk, lean sea fish, and meat. Vegetables, fruits and any vegetables will also be useful.
physical therapy
The complex of physiotherapy exercises contains special exercises aimed at increasing the mobility of the problem area of the spine, removing unnecessary stress on some elements of the skeletal system and eliminating muscle spasms in the cervicothoracic region.
To perform the exercises, you will need a gymnastic stick and a mat. Clothing should be as comfortable as possible and not restrict movement.
Before starting classes, to warm up the muscles, it is recommended to do a warm-up: slowly and alternately, swinging the legs and arms and turning the torso, pelvis and head in different directions. If the movement of the body causes pain, it should be done more smoothly or stopped.
Examples of exercises for thoracic osteochondrosis:
- Starting position: lying on your stomach, hands behind your head. First you need to spread your elbows as much as possible, then raise your shoulders and body. Hold this position for three seconds. Do the exercise 5 times in a row.
- Starting position: similar. Put your hands behind your back, fold your palms into the lock. Bend over, trying to raise your arms. Hold for three seconds. Perform at least 5 times.
- Position: standing on the floor, feet shoulder-width apart. Put your hands on your shoulders: left to left shoulder, right to right. Raise your shoulders in turn, directing your head in the direction of movement. Run 10 times.
- Lie on your stomach, stretch your arms forward. Raise your body. Perform 5 times in a row. Then put your hands along the body and lift the body too.
- Sit in a chair, holding a gymnastic stick in front of you. Take a deep breath as you straighten your body. On exhalation, the hands with the bullet kneel, the torso bends forward. Run several times.
- Standing on the floor, put your hands with a gymnastic stick on your shoulders. Twist your body to the right, then to the left 10 times.
- Sit in a chair, lean back. Bend strongly, using the thoracic region. Perform at least 10 movements.
This exercise can be done at home. But first, it is highly recommended that you get permission from a specialist.
Methods of traditional medicine
Folk remedies will help to cope faster with the manifestations of thoracic osteochondrosis.Medicines based on natural active ingredients are successfully used as adjuvant therapy. Some effective recipes:
- Rub for external use. It is prepared as follows: in equal parts, you need to take dandelion root, peppermint leaves, birch buds, coriander. Chop the ingredients and mix. So 3 tbsp. L. mix (with a slide), pour half a glass of boiling water and put on a slow fire for 5 minutes. Cool, add 75 g of butter and 75 g of sunflower oil. Cook for another 15 minutes. Scrub problem areas, then dress or wrap immediately.
- Gadget. For their preparation you can use fresh horseradish juice, bitter steamed herb wormwood or flaxseed.
- Painkiller. Prepared like this: 2 tbsp. L. chamomile color should be poured with 350 ml of boiling water and put on a slow fire for 5 minutes. Then cool, strain. Take 125 ml 3 times a day after meals.
- Rub the hops. For cooking in equal parts take: hop cones, ground into powder and melted lard. The ingredients are mixed. Used as a rub to relieve muscle tension.
All these medicines are prepared at home, but you can use them to treat the disease only after consulting a specialist.