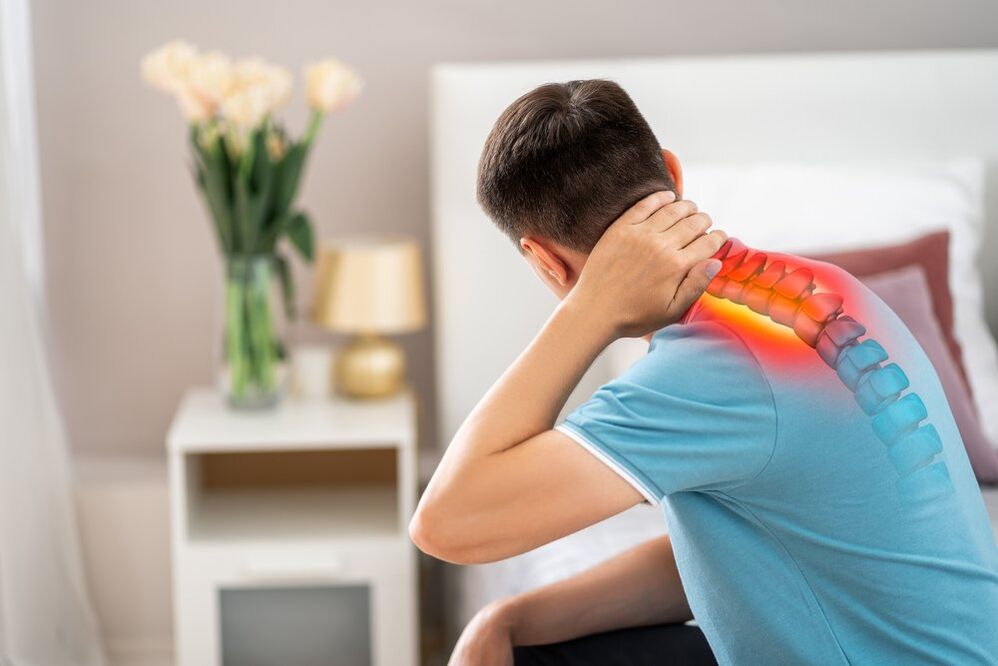
Osteochondrosis is a disease of the musculoskeletal system, manifested by the thinning of the bones and cartilage of the joints. Most often, patients are diagnosed with osteochondrosis of the spine, in which there is a destruction of the intervertebral discs in the cervical, lumbar or thoracic region. Intervertebral cartilage is needed to cushion movements and reduce the load on bone tissue, so the destruction of the discs leads to gradual damage to the vertebrae and deformation of the spine. Osteochondrosis can be a complication of an injury, a long-term violation of posture or another pathological condition. Treatment of the disease involves manual therapy, physiotherapy, and surgery for significant spinal deformities.
Osteochondrosis is one of the most common diseases of the musculoskeletal system in the elderly. In adolescents and young adults, the condition is diagnosed less frequently. Symptoms characteristic of the disease, doctors include severe pain in the affected joint area and reduced mobility. Without treatment, osteochondrosis can be complicated by spinal cord compression and internal organ dysfunction.
Symptoms of osteochondrosis
Manifestations of the disease depend on the area of destruction of the joint discs. The main symptom is aching or sharp pain, aggravated during movement. For this reason, patients often take a forced position. With osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, it is difficult for the patient to look around, severe headaches occur. If the disease is complicated by compression of the peripheral nerves and spinal cord, symptoms of movement disorders and disorders of the functions of internal organs occur.
Other symptoms and signs:
- Moderate dull pain during the day, aggravated during movements;
- The spread of pain in the head, shoulder, pelvis and lower limbs;
- Constant tension of the muscles associated with the affected intervertebral joint;
- Decreased performance;
- Sleep disorders;
- Change of posture and awkward gait.
If these symptoms occur, it is recommended that you make an appointment with your doctor. Timely advice will avoid negative consequences for your health.
The disease can progress for several years. The early stages of cartilage damage show no symptoms, but gradually there is constant pain.
Causes of osteochondrosis
Normally, the intervertebral cartilage is continuously supplied with blood and receives enough nutrients from the blood to renew cells and maintain its structure. With the aging of the tissues, degenerative changes can occur, characterized by insufficient cell renewal. Violation of blood flow occurs when the arteries are squeezed against the background of a permanent curvature of the spine or injury. Also, osteochondrosis can be the result of excessive physical exertion.
Causes of the disease:
- Gradual destruction of the intervertebral cartilage due to impaired posture, heavy lifting and movement patterns. The reason for the violation of the structure of the intervertebral discs can also be wearing shoes with a flat sole for a long time;
- Craniovertebral anomalies - a violation of the relative position of the structures of the cervical spine and skull. In this case, squeezing of blood vessels and reduced blood supply to tissues often occurs.
- Metabolic disorders, accompanied by insufficient formation of hydrophilic cartilage components;
- Inflammatory or autoimmune damage to cartilage, in which the body's defense system attacks healthy tissues;
- A herniated disc is a disease characterized by the displacement of cartilage and the protrusion of the disc in the spinal canal.
Clarifying the cause of osteochondrosis is important in choosing the right treatment.
Osteochondrosis Diagnosis
When the symptoms of osteochondrosis appear, it is necessary to make an appointment with a neurologist. The clinic doctor asks the patient for complaints and reviews the history to identify risk factors for the disease. A general examination is then performed to identify external signs of osteochondrosis and rule out symptoms of spinal cord dysfunction. To confirm the diagnosis, the neurologist prescribes special examinations.
Methods for diagnosing osteochondrosis:
- Spinal X-ray. The neurologist appoints this study to obtain an image of the affected segment of the spine in two projections. Before the procedure, the patient is asked to undress to the waist and stand in front of the machine. The resulting images allow the doctor to detect a hernia or other pathology, as well as determine the degree of damage to the vertebrae and intervertebral disc;
- MRI is a more informative study that allows a neurologist to study layered images of the spine in different projections. During the examination, the patient is asked to remove all metal jewelry and lie down on the tomographic table. The diagnostics take anywhere from 15 minutes to an hour. This is a painless and reliable method of diagnosing osteochondrosis. The results of an MRI scan allow you to immediately rule out other diseases with similar symptoms, such as tuberculosis of the bones or a malignant tumor. If MRI is contraindicated, myelography is indicated.
- Examination of the subarachnoid space of the spinal cord (myelography). The neurologist prescribes this procedure to exclude syringomyelia, oncology and other pathological conditions of the meninges. The method of obtaining an image does not differ from conventional radiography, however, before the study, the doctor injects a contrast agent into the subarachnoid space. Before the puncture, the doctor treats the skin with an antiseptic and anesthetizes the tissues. The needle is inserted into the intervertebral space of the lumbar spine.
In a specialized clinic, safe and reliable diagnostic tests are performed, which allow you to quickly start treatment of osteochondrosis.
Therapeutic treatment of osteochondrosis
The treatment is carried out after consultation with a neurologist and an orthopedist. In case of instability of the affected cervical segment of the spine, a Shants collar is applied. A prefabricated orthopedic collar is applied to the neck and reinforced with bandages. Wearing a collar is necessary to relieve the load on the affected spine and prevent the development of complications. In severe osteochondrosis of the lumbar or thoracic spine, the patient needs rest. The clinic doctor will also prescribe symptomatic therapy and physiotherapy to alleviate the patient's condition.
Treatment methods for osteochondrosis:
- Prescribe non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs to relieve pain. The neurologist prescribes nimesulide, celecoxib or another agent. It is necessary to strictly control the dosage of analgesics and monitor the state of the liver with prolonged use of painkillers.
- Traction therapy is a method of lengthening the spine in order to increase the intervertebral space to eliminate the squeezing of blood vessels and nerves. Before the procedure, a massage is performed to relax the muscles. The traction is performed on a special table or in a bathtub. The device is fixed on the patient's body in the desired position and gently stretches the spine. This is a very effective and safe procedure for the treatment of osteochondrosis.
- The use of anticonvulsants for complications of osteochondrosis. A neurologist prescribes a short course of carbamazepine or another drug to a patient.
- The use of muscle relaxants. These medicines relax the muscles associated with the affected area of the spine and relieve pain;
- Use of corticosteroids for nerve compression. These drugs relieve the inflammatory process in the tissues, which includes therapeutic massage, special exercises and warm-up.
The neurologist selects an individual treatment regimen for osteochondrosis, focusing on the patient's condition. Strict medical control of the course of treatment allows you to obtain the best prognosis.
Surgical treatment of osteochondrosis
If the diagnostic results reveal an intervertebral hernia or severe compression of the spinal canal, the patient should consult a neurosurgeon. The doctor assesses the severity of the identified pathology and, if necessary, performs surgery.
Surgical treatment options:
- Partial or complete removal of the intervertebral disc.The operation is performed under anesthesia. After applying anesthesia, the neurosurgeon treats the surgical field with an antiseptic and cuts the skin at a predetermined point. After pushing the muscle layer with a special tool, the doctor removes the affected intervertebral disc. If necessary, removal of the vertebral arch is also performed. Plastic surgery of the spinal segment is performed with transplantation of artificial materials. This effective operation is suitable for the treatment of intervertebral hernia and to relieve the symptoms of osteochondrosis;
- Interventions for the narrowing of the spinal canal.This surgery eliminates compression of the nerves and spinal cord. After applying the anesthesia, the doctor treats the surgical field with an antiseptic and makes a wide skin incision. Pushing back the muscle layer, the neurosurgeon reaches the intervertebral joint and performs the manipulation. The surgery involves the removal of the vertebral arch or the entire joint. The use of X-rays and microsurgical control allows you to perform the operation with minimal risk.
The most complex surgical interventions are performed in the surgical department of modern clinics.